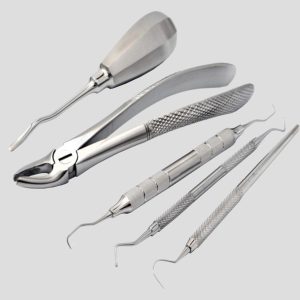
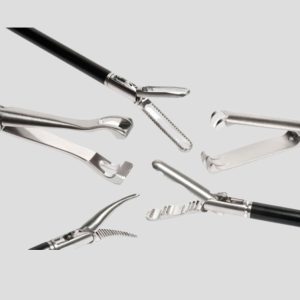
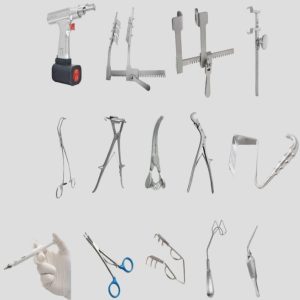
Milling is a precision machining process that removes material from stainless steel blanks to achieve the exact shape, grooves, or fitting required in surgical instruments. Understanding the full scope of milling is crucial, as high-accuracy milling is essential to meet medical-grade performance, hygiene, and safety standards.
Why Accuracy in Milling Matters
1. Instrument Functionality
Precise milling ensures jaws close tightly, scissors cut cleanly, and forceps align perfectly.
Even a 0.1 mm error can result in malfunction or failure during surgery.
2. Fit & Assembly
Many surgical instruments are multi-part assemblies (e.g., forceps, clamps, rongeurs).
Accurate milling ensures perfect hinge alignment, smooth movement, and tight tolerances.
3. Repeatability in Mass Production
CNC milling ensures every unit is identical across thousands of pieces.
Essential for batch consistency, especially when instruments are paired (e.g. matching jaws or jointed parts).
4. Cleanability & Sterilization
Smooth, uniform milled surfaces prevent fluid buildup and bacterial colonization.
Sharp corners or inaccurate grooves can trap debris or resist sterilization.
5. Surgeon Comfort & Performance
Ergonomically milled handles and grips improve precision handling, especially during long procedures.
Poorly milled parts lead to surgeon fatigue or instrument rejection.
What Rigor Instruments Ensures
| Precision Factor | Rigor’s Practice |
|---|---|
| Tolerances | Maintained within ±0.02 mm using 5-axis CNC milling |
| Tool Quality | High-speed carbide tools with auto-calibration |
| Surface Finish | Polished post-milling to reduce roughness (< Ra 0.4 μm) |
| Inspection | 100% digital inspection of critical dimensions |
Risks of Poor Milling Accuracy
| Problem | Impact |
|---|---|
| Misaligned jaws | Incomplete grasp, tissue trauma, or slippage |
| Uneven blade edges | Dull cuts, bleeding risk, or surgical failure |
| Loose pivot joints | Rattling instruments, imprecise motion |
| Sharp Grooves | Infection risk , Sterilization Failure |
Milling Machinery Used by Rigor Instruments
1. 5-Axis CNC Milling Machine
Brand/Model: HAAS UMC Series / DMG MORI
Purpose: Complex 3D contours, angled cuts on jaws, handles, and tips
Accuracy: ±0.01 mm
Use: Micro-serrations, ergonomic shaping, joint seat formation
2. 3-Axis Vertical CNC Milling Machines
Brand/Model: Fanuc / Mazak VCN Series
Purpose: High-speed precision flat milling and slotting
Use: Jaw edges, grooves, box locks, and screw seat milling
Features: Automatic tool changers, probing, and coolant systems
3. Mini CNC Milling Machines
Purpose: Ideal for small instruments (ophthalmic, dental, microsurgery tools)
Precision: ±0.005 mm
Use: Fine slots, hinge areas, and micro components
4. High-Speed Dental Milling Units
Use: For high-accuracy dental tools and implant-grade parts
Material Compatibility: 420, 316L, titanium
5. Wet Milling Systems
Purpose: Coolant-based systems to prevent heat stress during fine milling
Benefit: Maintains metal temper and smooth surface finish
6. CNC-Controlled Jig Milling
Use: For guided drilling, slotting, and bridge cutting in complex assemblies
Advantage: Used for custom instrument development and prototyping
🔧 Rigor Instruments Milling Capabilities Summary
| Machine Type | Application | Precision |
|---|---|---|
| 5-Axis CNC Mill | Complex shapes, angulated jaws | ±0.01 mm |
| 3-Axis Vertical Mill | Flat faces, slots, and box locks | ±0.02 mm |
| Mini CNC Mill | Microsurgery & ophthalmic tools | ±0.005 mm |
| Jig Mill | Custom and modular component machining | ±0.015 mm |