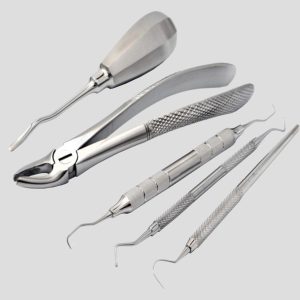
Outer Trimming & Ring Trimming in Forceps – Full Process
What Is Outer Trimming?
Outer trimming refers to shaping the outer contour of forceps, especially the handles, tips, and jaw area, after the forging stage.
Process:
Marking Template – A tracing guide or CNC program defines the forceps outline.
CNC Milling / Manual Grinding – Excess metal around the forged blank is trimmed away using:
Belt grinders
Rotary tools
High-speed burrs
Fine Shaping – Smooth curves, tapers, and joint edges are formed.
Polishing Prep – Trimmed areas are finished to reduce burrs or sharp transitions.
Purpose:
Achieve uniform outer dimensions
Prepare instrument for jointing and ring shaping
Ensure proper symmetry
What Is Ring Trimming?
Ring trimming focuses on refining the finger rings of forceps and scissors for:
Comfort
Size accuracy
Aesthetic symmetry
Process:
Initial Drilling – Finger holes are drilled to rough size (e.g., 16–20 mm).
Ring Cutting Dies or CNC – Tools are used to define the inner profile of the ring.
Hand Finishing / Lapping – Skilled craftsmen use files and rotary stones to:
Smooth inner ring walls
Remove burrs
Ensure ergonomic feel
Final Polish – Mirror finish applied to inner and outer ring surface
Rigor Instruments’ Expertise in Trimming Processes
Precision Engineering
CNC-controlled shaping ensures consistent geometry across batches.
Forceps are trimmed with tolerance of ±0.05 mm for exact matching in pairs.
Custom Ring Sizes
Available in standard and customized ring sizes for different surgical specialties (pediatric, plastic surgery, general, etc.)
Ergonomic Standards
Rigor ensures smooth, rounded inner ring edges to prevent finger fatigue.
Outer trimming shapes are validated by surgical technicians before production runs.
Quality Workflow
| Stage | Machine/Technique | QC Method |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Trimming | Belt Grinder + CNC | Shape template & digital caliper |
| Ring Punch & Trim | CNC lathe + manual filing | Ring gauge & manual inspection |
| Polishing & Finishing | Buffing wheels + vibro | Glove test & surface polish test |
General Precautions During Trimming
1. Maintain Symmetry
Ensure equal trimming on both halves of the forceps or scissors to prevent imbalance.
Use templates or CNC reference models for consistent shapes.
2. Avoid Over-Trimming
Removing too much material can:
Weaken the structure
Misalign joints
Lead to scrap loss
Operators must regularly measure during grinding or cutting.
3. Use Proper Tools
Always use sharp, well-maintained grinding and cutting tools.
Worn tools can cause burns, uneven surfaces, or chatter marks.
4. Prevent Heat Damage
Excessive grinding can generate heat, which:
Affects hardness and temper of stainless steel
Causes discoloration or micro-cracks
Use coolants or take breaks during prolonged trimming.
Safety & Handling Precautions
| Precaution | Why It’s Important |
|---|---|
| Wear cut-resistant gloves | Prevent injury from sharp edges or burrs |
| Use eye protection | Protect against flying metal shavings |
| Clamp instrument securely | Prevent kickback or tool slippage |
| Maintain clean workspace | Avoid mix-up or accidental damage of components |
Quality Control Precautions
Frequent Measurements: Use digital calipers and ring gauges after trimming
Visual Checks: Look for:
Sharp edges
Asymmetry
Burn marks
Surface roughness
Test Fit: Ensure the trimmed piece aligns properly with mating parts before assembly
How Rigor Instruments Ensures Safe Trimming
Skilled Craftsmen: All trimming is done by trained technicians with years of experience
Tool Calibration: Trimming tools are calibrated and maintained weekly
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Followed strictly for every instrument category
Post-Trimming Inspection: Every piece is manually inspected and digitally logged