Introduction
The scalpel is one of the most iconic and indispensable tools in the medical field. It is a small, extremely sharp bladed instrument used for making precise incisions during surgical and medical procedures. From minor outpatient operations to complex surgeries, scalpels are a staple in almost every clinical setting.
Types of Scalpels
Scalpels can be classified by blade design, handle type, and sterility:
1. Reusable Scalpels
Consist of a reusable handle with detachable blades.
Commonly used in hospitals and operating theaters.
Sterilized after each use.
2. Disposable Scalpels
Single-use with a plastic handle and pre-attached blade.
Frequently used in outpatient settings, dermatology, and emergency rooms.
3. Safety Scalpels
Feature retractable or shielded blades to reduce accidental injuries.
Common in high-traffic environments like ERs and teaching hospitals.
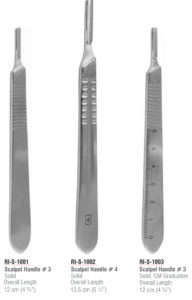
Common Blade Types and Their Uses
| Blade No. | Description | Compatible Handle | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| #10 | Curved edge | No. 3 | Large skin incisions |
| #11 | Pointed tip | No. 3 | Precise puncture/stab incisions |
| #12 | Hooked | No. 3 | ENT surgeries, suture removal |
| #15 | Small curved | No. 3 | Delicate, short incisions |
| #20–22 | Large curved | No. 4 | Orthopedic and general surgery |
Uses of Scalpels in Medicine
Scalpels are widely used across various specialties:
1. General Surgery
Used to make primary incisions in the skin and deeper tissues.
Critical in procedures like appendectomy, hernia repair, and cholecystectomy.
2. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
For fine, controlled cuts with minimal tissue trauma.
Helps achieve precise cosmetic outcomes.
3. Dermatology
Used in procedures like mole removal, biopsies, and excision of skin lesions.
4. ENT (Ear, Nose, Throat) Surgery
Delicate blades like #12 are used for tonsillectomies or nasal surgeries.
5. Ophthalmology
Extremely fine scalpels assist in eye surgeries such as cataract or corneal procedures.
6. Orthopedic Surgery
Larger blades are employed to cut through thick skin, fascia, and even cartilage.
7. Veterinary Medicine
Scalpels are essential in animal surgeries, both minor and major.
Advantages of Using Scalpels
Precision: Offers clean and sharp cuts.
Control: Allows surgeons to maneuver easily around delicate structures.
Reduced Tissue Damage: Minimal collateral damage compared to scissors or cautery.
Fast Healing: Clean incisions promote better wound healing.
Safety and Handling
Proper usage and disposal of scalpels are critical:
Always use with a blade remover or forceps.
Dispose of used blades in a designated sharps container.
Use safety scalpels where possible to reduce risk of injury.
Key Features
Ultra-sharp stainless steel blades
Ergonomic handles for maximum control
Available in both reusable and sterile disposable formats
Color-coded safety options for staff protection
Compatible with standard No. 3 and No. 4 handles
Packaging Options
Box of 10, 50, or 100 (blades or scalpels)
Bulk OEM packaging for hospitals and distributors
Custom branding available upon request
Safety & Compliance
CE Marked
ISO 13485:2016 Certified
Latex-free and hypoallergenic materials
📞 Order Now
Enhance surgical precision with our premium range of scalpels.
Contact Us for custom branding, OEM orders, or bulk pricing.
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +92-303-7759000
Conclusion
Scalpels remain one of the most vital instruments in medical practice. Their unmatched precision, versatility, and efficiency make them essential in virtually all surgical disciplines. Understanding the types, applications, and safety considerations ensures optimal outcomes for both patients and medical professionals.