Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MIS) offers several significant benefits over traditional open spine surgery. Here are the key advantages:
1. Smaller Incisions
Less damage to skin and muscles
Reduced risk of infection and scarring
2. Less Blood Loss
Due to minimal tissue disruption
Decreased need for blood transfusions
3. Reduced Postoperative Pain
Minimal muscle cutting leads to less pain
Lower dependence on opioids or pain medications
4. Shorter Hospital Stay
Many procedures are outpatient or require only 1–2 days in hospital
Faster return home and lower medical costs
5. Quicker Recovery Time
Faster return to work and daily activities
Athletes and active individuals benefit from early rehabilitation
6. Lower Risk of Complications
Reduced risk of infections, deep vein thrombosis, and other surgery-related complications
7. Precision with Advanced Technology
Often performed using intraoperative imaging (CT, MRI, navigation systems)
More accurate placement of screws, implants, and decompression
8. Cosmetic Advantages
Smaller scars
Better aesthetic outcomes, especially for younger patients
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MIS) is performed using advanced techniques and specialized instruments that allow surgeons to access the spine with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues. Here’s a simplified step-by-step overview of how it is typically done:
Step-by-Step: How MIS Spine Surgery Is Performed
1. Preoperative Imaging and Planning
Surgeons use MRI, CT scans, or fluoroscopy to pinpoint the exact location of the problem (e.g., herniated disc, spinal stenosis, fracture).
The surgical plan is created using navigation systems or robotic assistance.
2. Patient Positioning
The patient is positioned based on the surgical site (prone or lateral).
Padding and support devices ensure stability and safety during the procedure.
3. Small Incision
A small incision (usually 1–2 cm) is made over the target area.
Unlike open surgery, muscles are not cut but gently spread using dilators.
4. Tubular Retractor Insertion
A series of dilators create a tunnel through muscle to the spine.
A tubular retractor holds this tunnel open, providing access to the surgical site.
5. Use of Endoscope or Microscope
A camera (endoscope) or surgical microscope provides high-definition, magnified visuals.
Surgeons operate through the tube using long, specialized instruments.
6. Surgical Correction
Depending on the case, the surgeon may:
Remove herniated disc material (discectomy)
Decompress nerves (laminotomy or foraminotomy)
Stabilize vertebrae (spinal fusion with screws and rods)
Remove tumors or treat fractures
7. Closure
The tubular retractor is removed.
The small incision is closed with a few sutures or surgical glue.
No large muscle dissection or bone removal is involved.
Postoperative Care
Patients often walk within hours of surgery.
Hospital stays are short (often same-day or 1–2 nights).
Recovery time is significantly reduced compared to open surgery.
Instruments Used In MIS Neuro Spine Surgery
1. Dilator Set
Series of sequential tubular dilators
Used to gently separate muscle fibers without cutting
Creates a pathway to the spine
2. Tubular Retractor System
Expandable or fixed tubular retractor
Holds open the working channel
May be radiolucent for imaging
3. Endoscope or Surgical Microscope
For high-resolution visualization inside the narrow space
Often used with a light source and camera system
4. MIS Hand Instruments
Disc Rongeurs / Pituitary Forceps – for disc removal
Kerrison Rongeurs – for bone or ligament removal
Curettes – for scraping or cleaning
Nerve Root Retractors – to protect neural structures
Nerve Hooks and Dissectors
5. High-Speed Burr / Drill System
Removes bone precisely for decompression or access
6. MIS Spine Fusion Instruments
Pedicle Probe & Sounder
Guidewires (K-wires) – for screw insertion
Tap and Screwdriver System – for percutaneous pedicle screw placement
MIS Rod Inserter and Manipulators
7. C-arm Compatible Instruments
All tools are designed for use under fluoroscopic (X-ray) guidance
Radiolucent materials often used
8. Hemostasis Tools
Bipolar cautery or RF probes – to control bleeding
Suction irrigation cannulas
9. Closure Instruments
Skin staplers or suture kits
Minimal closure required
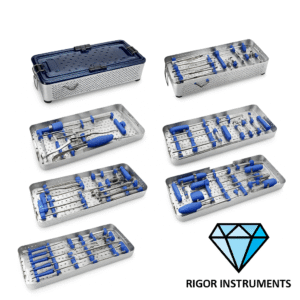
Experience Precision with Rigor Instruments’ Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery Sets
Rigor Instruments proudly presents its state-of-the-art Minimally Invasive Spine (MIS) Surgery Sets—engineered for accuracy, efficiency, and minimal tissue disruption. Each set includes high-quality tubular retractors, sequential dilators, ergonomic hand instruments, and radiolucent components, designed to meet the highest surgical standards. Trusted by spine specialists worldwide, our MIS sets support faster recovery times, reduced surgical trauma, and outstanding intra operative control. With durable German-grade stainless steel and rigorous quality control, Rigor Instruments delivers the reliability your OR demands.
Choose Rigor Instruments—where innovation meets precision in spinal care.
To Order High quality MIS Surgery Sets Contact us at:
Email: [email protected]
whats app :+92-3037759000